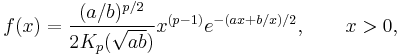Generalized inverse Gaussian distribution
| Parameters | a > 0, b > 0, p real |
|---|---|
| Support | x > 0 |
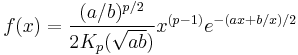 |
|
| Mean | 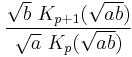 |
| Mode | 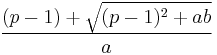 |
| Variance | ![\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)\left[\frac{K_{p%2B2}(\sqrt{ab})}{K_p(\sqrt{ab})}-\left(\frac{K_{p%2B1}(\sqrt{ab})}{K_p(\sqrt{ab})}\right)^2\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/1731dfd5cec681cbb78eb499a7c9c358.png) |
| MGF | 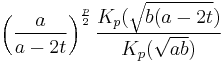 |
| CF | 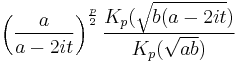 |
In probability theory and statistics, the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution (GIG) is a three-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with probability density function
where Kp is a modified Bessel function of the second kind, a > 0, b > 0 and p a real parameter. It is used extensively in geostatistics, statistical linguistics, finance, etc. This distribution was first proposed by Etienne Halphen.[1] It was rediscovered and popularised by Ole Barndorff-Nielsen, who called it the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution, and Herbert Sichel. It is also known as the Sichel distribution. Its statistical properties are discussed in Bent Jørgensen's lecture notes.[2]
The inverse Gaussian and gamma distributions are special cases of the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution for p = -1/2 and b = 0, respectively.
Entropy
The entropy of the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution is given as ![H(f(x))=\frac{1}{2} \log \left(\frac{b}{a}\right)%2B\log \left(2 K_p\left(\sqrt{a b}\right)\right)-
(p-1) \frac{\left[\frac{d}{d\nu}K_\nu\left(\sqrt{ab}\right)\right]_{\nu=p}}{K_p\left(\sqrt{a b}\right)}%2B\frac{\sqrt{a b}}{2 K_p\left(\sqrt{a b}\right)}\left( K_{p%2B1}\left(\sqrt{a b}\right) %2B K_{p-1}\left(\sqrt{a b}\right)\right)](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/e0e880a1a9828da648dd19ba87014578.png)
where ![\left[\frac{d}{d\nu}K_\nu\left(\sqrt{a b}\right)\right]_{\nu=p}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/b945f4e904eb1e6d38f1bd7850589a29.png) is a derivative of the modified Bessel function of the second kind with respect to the order
is a derivative of the modified Bessel function of the second kind with respect to the order 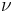 evaluated at
evaluated at 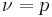
References
- ^ Seshadri, V. (1997). "Halphen's laws". In Kotz, S.; Read, C. B.; Banks, D. L.. Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, Update Volume 1. New York: Wiley. pp. 302–306
- ^ Jørgensen, Bent (1982). Statistical Properties of the Generalized Inverse Gaussian Distribution. Lecture Notes in Statistics. 9. New York–Berlin: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-90665-7. MR0648107.